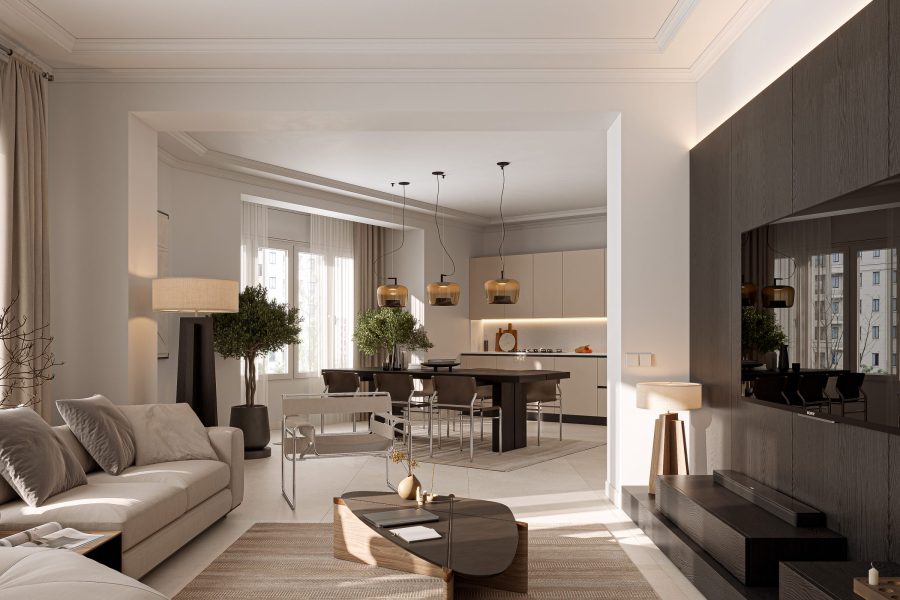
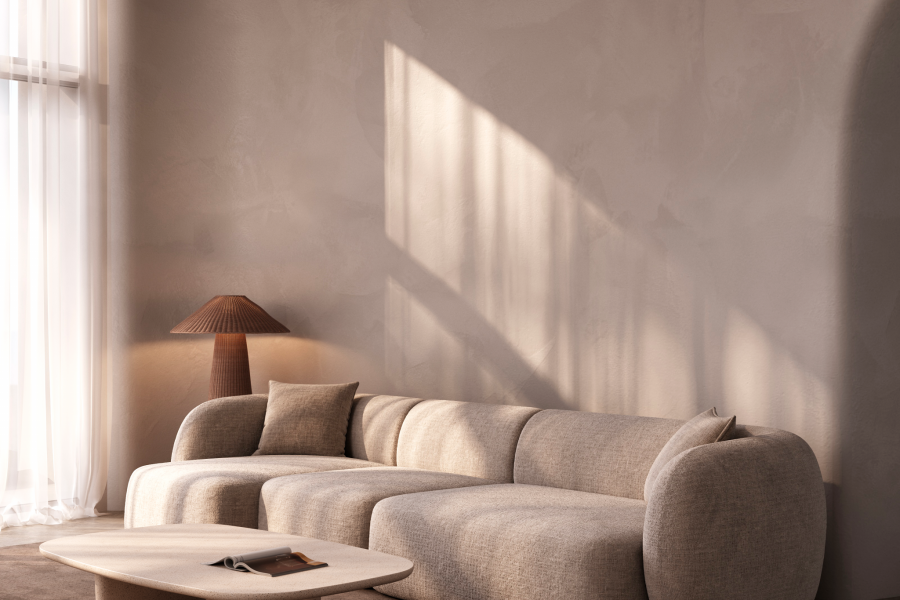
3D Architectural Visualization
We craft linear, easy-to-follow presentations for residential and commercial projects with hyper-real results
Your visual challenges deserve a vision that truly hits the mark.
Every render is born from a strategic vision, refined over years of practice, where technical precision and signature design converge to turn your project into a timeless experience.
Immediate start



Outsource to scale
Outsource your visualisation and free your team from operational tasks. We handle modelling, lighting and materials, assigning you a dedicated project manager for quality control; you set the direction, we execute with firm deadlines.Project development
Skip the heavy lift. We take full ownership of render development, from material setup and lighting to model refinement, so your team can stay focused on design and delivery.Architectural presentation
Ideal for renovations, competitions, and client boards. Clear composition, photoreal views, and believable scale help stakeholders understand the design fast. Go-to-market assets.Pitch to investors
Launch-ready stills, animations, and tours that drive presales, lift investor presentations, and secure buy-in.
Delegate to scale
Outsource your visualisation and free your team from operational tasks. We handle modelling, lighting and materials, assigning you a dedicated project manager for quality control; you set the direction, we execute with firm deadlines.
Project development
Skip the heavy lift. Ideal for competitions, juries and client presentations.
Architectural presentation
Visual assets aligned with your identity, ready for web, dossiers and competitions. Clear composition, photoreal views, and believable scale help stakeholders understand the design fast.
Go-to-market assets
Presentations built for decision-makers: consistent images, straightforward data, and timelines that show each stage.Every image is born to push the boundaries of realism and unveil the essence of your project
Every architectural idea begins as an emotion; a sense of space, light, and possibility. 3D architectural visualisation gives form to that feeling, transforming abstract plans into immersive, photorealistic experiences that can be seen, felt, and imagined.
But beyond its visual beauty, 3D visualisation becomes a language, one that helps architects make confident decisions, investors see potential, and clients connect emotionally with spaces that don’t yet exist.
Lighting studies and advanced texturing ensure that architectural renders rigorously reflect materials, proportions and construction solutions, supporting decision-making in preliminary design, competitions and technical presentations.
High-impact exterior visualisation
Millimetre precision and cutting-edge technology to bring your project to life.
High-impact exterior visualisation
Millimetre precision and cutting-edge technology to bring your project to life.
Do you need 3D renders for your project?
Get your quote within 24 hours
Workflow, made effortless
01
Brief intake and file check
02
Camera and perspective sign-off
We select with the client the angles with the greatest narrative and commercial potential, optimizing the visual impact of the rendering.
03
Work-in-progress reviews with your project manager
We model the project in detail, taking care of geometries, textures and finishes to achieve an accurate and realistic representation.
04
Final delivery of stills, animations, or tours.
Delivery of the images in 4K resolution (3840 × 2160 px), ready for presentation, marketing or publication.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is architectural visualisation?
What types of 3D render exist?
How do I get started with a 3D exterior render?
What is 3D interior rendering?
How do generic renders differ from architectural renders?
What is the cost of a 3D architectural render?
How long does an exterior render take?
What is the process like?
What software do you use?
Can you adapt to my studio’s render design?
What are the benefits of outsourcing architectural renders?
Can the delivery format be 8K?
Our projects are delivered in 4K as standard. If you need an upgrade to 8K, we can do that without any problem; it will be considered an additional service and quoted separately.





